Mastering Critical Thinking with Bloom's Taxonomy Verbs
Bloom's Taxonomy Verbs: A Guide to Enhancing Critical Thinking
What if there was a structured way to elevate your thinking skills? How can educators and learners systematically approach complex problems? Bloom's Taxonomy, a hierarchical model for classifying educational objectives, provides a powerful framework for critical thinking. At its core are actionable verbs that guide cognitive processes—from basic recall to advanced analysis and creation. This article explores how Bloom's Taxonomy verbs can transform learning and problem-solving.
Understanding Bloom's Taxonomy
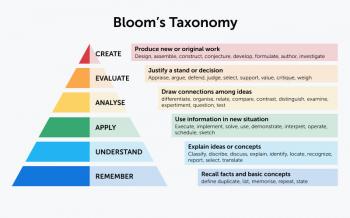
Bloom's Taxonomy, developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, categorizes cognitive skills into six levels: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Each level builds on the previous one, encouraging deeper engagement with content. The taxonomy was revised in 2001 to replace static nouns with dynamic verbs, emphasizing action-oriented learning.
Example: In a history class, students might remember key dates (Level 1), explain causes of an event (Level 2), and later design a mock treaty (Level 6).

The Power of Verbs in Learning
Verbs like summarize, compare, or critique serve as mental triggers. They clarify expectations and scaffold tasks. For instance, asking students to analyze a poem (Level 4) requires deeper thought than simply listing its themes (Level 1).
Practical Tip: Use verbs intentionally in assignments. Instead of "Write about climate change," try "Propose three solutions to mitigate climate change."

Applying Bloom’s Verbs in Education
For Teachers
Design lesson plans that progress through taxonomy levels. Start with define (Remembering) and culminate with construct (Creating).
For Students
Use verbs to self-assess understanding. Can you debate a topic (Evaluating), or only describe it (Remembering)?

Beyond Academia: Workplace Critical Thinking
Bloom’s verbs aren’t just for schools. In business, evaluating data (Level 5) or generating strategies (Level 6) drives innovation. A marketing team might analyze campaign metrics before creating a new ad concept.

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Avoid mismatching verbs to cognitive levels. For example, asking students to identify (Level 1) when the goal is evaluate (Level 5). Use verb charts as checklists.

Tools and Resources
- Printable verb posters for classrooms
- Digital apps like "Bloom’s Taxonomy Wheel"
- Workshops on writing learning objectives







